As developed nations turn away from coal-fired power, Chinese funding has helped the dirtiest fossil fuel take off in Pakistan.
Coal’s surge in the South Asian nation is symbolic of the difficult choice that the region’s developing countries face as they seek affordable energy to support economic growth while trying to limit chronic air pollution. Asian demand is expected to support the commodity as its usage drops in most of the developed world in a transition to cleaner or renewable energy sources.
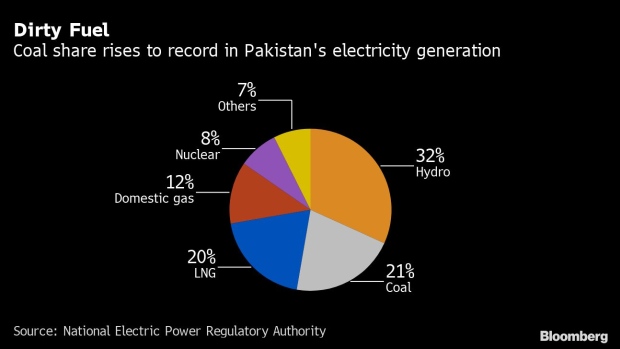
Pakistan’s coal-fired power generation jumped 57% to a record in the fiscal year through June, according to data from the government’s National Electric Power Regulatory Authority. Coal accounted for about a fifth of total output, backed by supplies from the country’s first coal mine in its Thar region, developed as part of China’s Belt and Road plan.
Coal is set to expand further as China pushes funds into building more power plants in the country and mines to feed them. Pakistan is one of the flagship markets for China’s Belt and Road initiative, with more than $70 billion of projects including coal and liquefied natural gas fired power plants helping the nation end decades of electricity shortfalls.
“China has been cutting back on coal at home but it has no compunction about using coal in things that it funds outside of China,” said James Dorsey, a senior fellow at the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies in Singapore. “Chinese can be willing but they need a partner to go along with them. In this case it’s the Pakistani government.”
Belt and Road progress has slowed recently with overseas energy spending last year dropping to the lowest in a decade, dogged by accusations that China is luring poor countries into debt traps for its own political and strategic gain. China’s President Xi Jinping has publicly urged more clean energy as part of the program, and the plan found new life in Pakistan recently with an agreement to build two hydro-power generation projects.
Until 2016, Pakistan had just one coal-burning power plant. It now has at least nine and more are in the making. The first target of these plants has been to replace expensive fuel oil-based generation facilities that burdened the nation’s economy with heavy costs and pollution.
The rise in coal power has come because of supplies from the Thar coal mine, Power Ministry spokesman Zafar Yab Khan said. The country will balance rising coal use with more renewable energy and its coal plants will use low-emissions technology, he said.
With the shift to coal, average generation costs dropped 11% during the fiscal year, according to data from Karachi-based brokerage Arif Habib.
“Pakistan has increased coal-based generation to make it its new base to replace its previous expensive fuel oil-powered power plants,” said Tahir Abbas, head of research at Arif Habib. “This has also helped bring down the power prices, energy import bill and increase the share of an indigenous energy source.”